Sit up
Posture is the way you hold yourself as you row.
Good rowing posture has the pelvis in a neutral position i.e. tilted in line with the lower spine.
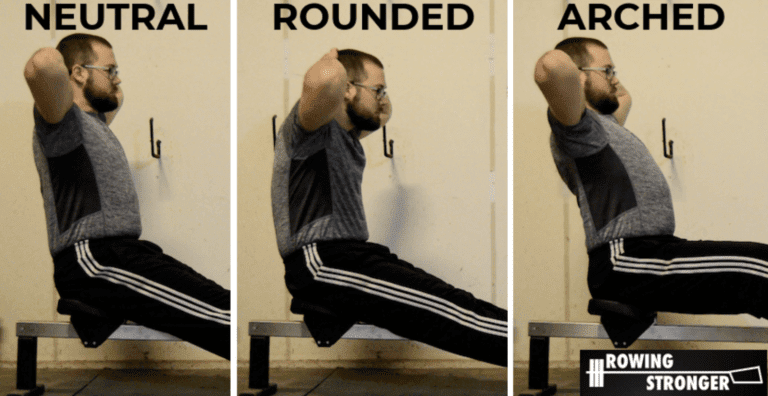
 Posture – neutral, rounded, arched. Image Credit: Rowing Stronger
Posture – neutral, rounded, arched. Image Credit: Rowing Stronger
- NEUTRAL – pelvis and lower spine aligned. Lower back is FLAT.
- ‘ROUNDED COUCH POTATO’ – pelvis tilted back more than lower spine. Lower back is BOWED, curved outwards.
- ‘ARCHED GYMNAST’ – pelvis is tilted further forward than lower spine. Lower back is HOLLOW, curved inwards.

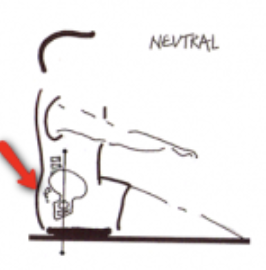
How to find the correct rowing posture for you
- Sit down on an erg or at the kitchen table – somewhere un-upholstered so that you can tell how much sagging is you and not the soft cushions. Slump a little, let your back relax. Now have someone press firmly on the top of your head. Push your head up against this hand until you are sitting tall. Notice how you lengthen your spine.
- Which muscles did you feel moving first?
- What happens to your shoulders as you push your head up more firmly?
That’s right – the higher you try to go the more you pull your shoulders down. It is a long lower back that makes you taller.
Good rowing posture requires core strength. If the athlete is weak and lacks control of the muscles in the core then sitting well is not possible for long periods.
Description of Good Posture
Good posture in sculling or rowing requires that the pelvis be in neutral position and the lower spine straight. The upper body is free to stretch forward during the recovery towards the catch and will be slightly rounded.
In order for the pelvis to be in the neutral position the athlete should sit well on the seat rather than on the front edge. The athlete should have contact between the upper thigh and the seat rather than the lower back and the seat.
- Sit on an erg in your usual TV-watching slumped position, feet unstrapped. Your tailbone will be somewhere near the middle of the seat and your back curved. Now stretch forward as far as you can.
- Where do your fingers reach to?
- How do the muscles round your shoulders and chest feel?
- What happens to your feet when you stretch forward?
Now roll forward until your shins are vertical.
- How far has your handle moved?
Go back to the finish position and shuffle back on the seat until your tailbone is at the back and you can feel the front of the seat against your hamstrings. Stretch forward again.
- There may be some protest from your hamstrings but how far can you reach forward now?
- How do the muscles round your shoulders and chest feel?
- What happens to your feet when you stretch forward?
Now roll forward again
- How long is your stroke now?
Benefits of a Good Posture
 Good rowing posture Photo Credit: Ben Rodford
Good rowing posture Photo Credit: Ben Rodford
Sitting towards the back of the seat allows the pelvis to tilt, increasing the range of movement in your lower back and increasing the length of your stroke.
Rocking your pelvis forwards brings your weight onto your feet adding to your poise and balance.
Using the pelvis and the muscles around it to stretch forward relaxes the upper body. This will make it easier to move your arms and thus control the blade as well as making it easier to breathe.
Moving the pelvis means that you’re using the large muscle groups around it; using them through a greater distance and making it possible for them to do more work generate more power and accelerate the boat better.